Author: Mr. Charalambos Papasavvas
Advocate – Legal Consultant
Managing Partner of PAPASAVVAS & LISKAVIDOU LLC
Founder of RELOTECH EXPERTS
Founder of NEOCOURSES INNOVATION CENTER
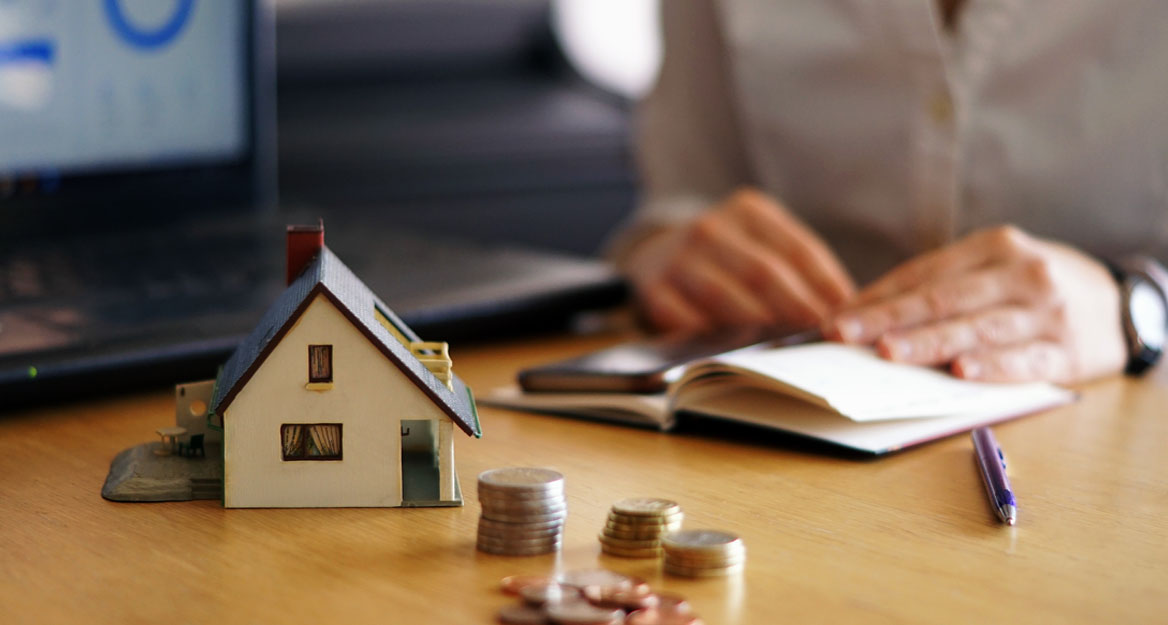
Rental property investment in Cyprus provides a solid avenue for generating passive income, but it comes with specific tax responsibilities that investors must understand to ensure compliance and profitability. Whether you’re a local or international property owner, grasping the tax implications of rental income is essential for effective financial management. This overview breaks down the key aspects of rental income taxation in Cyprus, helping you navigate the tax landscape and optimize your investment.
What is Rental Income Tax?
Rental income tax in Cyprus is the tax imposed on earnings from leasing out real estate properties. The tax is calculated on the gross rental income after subtracting allowable deductions, such as expenses for repairs, maintenance, loan interest for property acquisition, and management fees. This net income must be declared annually on a tax return and is
subject to progressive personal income tax rates. Understanding this tax is vital for property owners to ensure compliance and make informed financial decisions.
Why Understanding Tax Obligations Matters
For property owners in Cyprus, knowing the tax requirements tied to rental income is critical to avoid legal issues and penalties. Compliance with local tax laws ensures smooth operations and prevents unexpected financial burdens. Additionally, understanding deductions can lower your tax liability, boosting the profitability of your investment. For non-residents, the local tax system may differ significantly from their home country’s regulations, making it even more important to be well-informed.
Types of Taxes on Rental Income
Personal Income Tax
Rental income in Cyprus is subject to personal income tax for both residents and non-residents. An individual is considered a tax resident if they spend more than 183 days in Cyprus during the tax year. The tax rates are progressive: 0% for annual income up to €19,500, rising to 35% for income over €60,000. After allowable deductions, net rental income is combined with other taxable income and taxed at these rates. This cumulative approach highlights the importance of understanding your overall tax liability for effective financial planning.
Special Defence Contribution (SDC)
Cyprus tax residents who are also Cyprus-domiciled must pay SDC on rental income at an effective rate of 2.25% (3% on 75% of gross rental income). Non-domiciled residents and non-residents are exempt from SDC. A 2023 Cyprus Tax Authority circular clarified that rental income from self-catering accommodations rented via online platforms may be treated as
business income, subjecting it to personal income tax instead of SDC, under specific conditions.
General Healthcare System (GHS) Contributions
All Cyprus tax residents, regardless of domicile, must contribute to the GHS at 2.65% of gross rental income, with a cap on total annual income from all sources at €180,000. This applies to both residents and non-residents earning rental income in Cyprus.
Immovable Property Tax and Local Fees
The state-level Immovable Property Tax (IPT) was abolished in January 2017. However, local municipalities still impose an annual municipal tax based on the property’s value as of January 1, 1980, typically ranging from 0.1% to 0.2%. Property owners also face local fees for services like garbage collection, sewerage, and street lighting, which vary by municipality and should be factored into overall expense planning.
Tax Deductions for Rental Property Owners
Allowable Expenses
Property owners can deduct various expenses related to managing and maintaining rental properties, reducing their taxable income.
These include:
● Costs for repairs and maintenance, such as painting or fixing leaks.
● Interest on loans used to purchase or improve the property.
● Utility charges (e.g., electricity, water) not reimbursed by tenants.
● Management fees, including legal fees tied to leasing.
● Insurance premiums for the rental property.
● Local authority taxes and fees for services like garbage collection.These expenses must be directly related to generating rental income and supported by proper documentation.
Depreciation of Assets
Rental property owners can claim capital allowances (depreciation) on assets like furniture, fixtures, and structural improvements. For example:
● Furniture and fittings are typically depreciated at 10% per year using the reducing balance method.
● Structural improvements, such as a new roof, can be depreciated over their useful life. Consulting a tax professional is recommended to ensure accurate calculations and maximize these deductions.
Compliance with Cyprus Tax Laws
Filing Requirements
Rental income must be declared annually via a tax return, due by April 30 of the following year, even if no tax is owed. This applies to both residents and non-residents, who may need to register with Cypriot tax authorities if not already registered. All property owners with taxable income exceeding €19,500 must file, regardless of residency.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with tax regulations can result in:
● Fines for late or non-filed tax returns.
● Interest on unpaid taxes from the due date until payment.
● Additional taxes if under-reporting is uncovered during an audit. To avoid these penalties, maintain accurate records, file on time, and seek professional advice when needed.
Benefits of Proper Tax Management
Financial Savings
Effective tax management reduces taxable income through deductions, avoids penalties, and ensures you don’t overpay. Staying updated on tax rates and thresholds allows better financial planning and increased profitability.
Avoiding Legal Issues
Compliance prevents legal risks like audits or fines for tax evasion. Cyprus tax authorities enforce strict rules, and accurate reporting ensures you stay on the right side of the law.
Building a Positive Relationship with Authorities
Consistent compliance fosters trust with tax authorities, which can be helpful for resolving disputes or seeking guidance. A good reputation simplifies interactions and future dealings.
Tips for Maximizing Rental Income
Optimization Strategies
● Adjust rental rates to align with market trends, balancing competitiveness and tenant appeal.
● Upgrade and maintain properties regularly to increase value and attract higher-paying tenants.
● Consider short-term or vacation rentals, which may offer higher returns depending on location and demand.
Leveraging Tax Breaks
Take advantage of deductions for expenses and depreciation. Cyprus also offers incentives for renovations or energy-efficient upgrades, which can lower taxable income while enhancing property value.
Consulting Professionals
Tax laws can be complex and change over time. A tax advisor can provide tailored advice, keep you updated on regulations, and help optimize your tax strategy for maximum returns.
Conclusion
Understanding rental income tax obligations in Cyprus is essential for property investors to protect their investments and ensure compliance. By declaring income accurately, leveraging deductions, and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can minimize tax liabilities and maximize profitability. Staying informed and proactive ensures a successful and stress-free investment experience in Cyprus.